The digital TV smart card is to be used with a digital TV set-top box. The set-top box is equivalent to a card reader and can work like a computer. Since the digital TV smart card has a built-in processor and an interface to communicate with the digital TV set-top box, it also contains some integrated memory that allows the operator to download data and applications to the smart card. Therefore, digital TV smart cards are required to have a high degree of security to ensure that unauthorized users cannot access the services of various business items of the digital television system.
At present, the main function of the digital TV smart card is to be used for secure storage, decryption authorization and access rights, and to the set-top box. In the future application field of digital TV, the smart card can also be programmed to play the function of the electronic wallet for online shopping. And other business services such as instant payment.
The characteristics and types of a smart card
1. Features of the smart card
In today's network system applications, in addition to the characteristics of large capacity, stability, portability, and compatibility, smart cards have two most important features: personal identity and ciphertext.
The so-called personal identity means that the smart card can indicate the identity of the cardholder. Nowadays, in all kinds of transactions, the identity of the counterparty is finally confirmed. The smart card can conveniently indicate the identity of the cardholder through an ID (Identity) number stored in the card.
The so-called ciphertext means that the smart card can store some data in the form of cipher text. Some smart cards can also use their own microprocessor for dynamic data addition/decrease.
2. Type of smart card
Smart cards can be divided into contact smart cards and contactless smart cards according to the types of chips they embed. See Table 1.

Table 1
Contact smart cards are divided into two categories: read-only storage smart cards and microprocessor smart cards. See Table 2.

Table 2
3. Smart card file system
The file system of a smart card is like a tree file system of a computer DOS (disk operating system). According to the fourth part of the ISO (International Standards Organization) 7816 standard, the files of the smart card are divided into two types: DF (Dedicated File) and EF (Elementary File). The DF contains some control information, which can be the parent file of EF or DF, just like the directory file in DOS. EF is a collection of data units. It cannot be the parent file of any file. This is similar to the TXT (DOS file extension; is a normal ASCII text file) file in DOS.
The smart card file system has a required ROOT (root file), which is a DF file, generally called MF (Master File: Master File). Each file (including DF and EF) has a file ID number (two bytes). For example, the ROOT ID number is generally "3F00". If you want to read/write a file, you must first select the ID number of the file with the Select command. The file types of EF are: transparent EF, linear fixed length EF, linear variable length EF, and cyclic EF. The operation of the last three EF files is done by manipulating the records they contain.
Second, the international specification of smart cards - ISO 7816
ISO 7816 is an international standard that smart cards must follow. ISO 7816 specifies some physical properties of plastic materials used in smart cards, including temperature range, flexibility, position of electrical contacts, and ways to exchange information between the built-in microchip and the outside world. ISO The first part of the 7816 standard specifies that the contact smart card has a total of eight contacts (see Table 3) through which the smart card communicates with the outside world. The ISO 7810 standard specifies the size of a smart card. Up to now, the ISO 7816 standard has been released in nine parts. From Table 4, it can be clearly seen from the simple to the complex development path of the contact smart card.
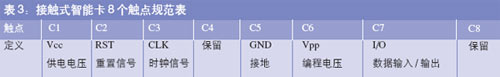
table 3
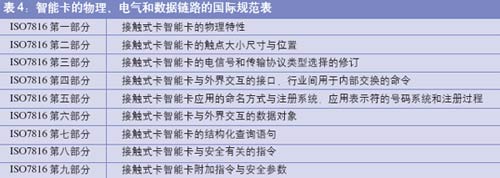
Table 4
Three digital TV reception smart card security
1. Basic security requirements for smart cards
Smart cards employ a number of security mechanisms. In general, the security mechanisms used for microprocessor cards are more complex than those used for read-only memory cards. But their basic security requirements are as follows:
(1) Physical secrecy
Physical secrecy actually limits the range of smart card users from the reading of information on the card. “Without special skills and tools, software and hardware cannot be added, deleted or replaced; input, storage or any unauthorized access/modification of sensitive data can only be achieved through effective spying; any part of the failure Or violent damage will not lead to the leakage of sensitive data."
Some smart cards, anyone can read the information on the card, then the card itself is a kind of protection. For example, a medical card that records the patient's name and blood type, such a smart card generally does not have a password, as long as the person who gets the card can read the information on the card.
For smart cards that only allow third parties to read information, only the card issuer can read the information on the card. For example, only the issuing institution can rewrite the information on the electronic wallet. These smart cards are now protected by a 16- to 32-digit password.
(2) logical confidentiality
Logical security is actually a way of reading information from a card to limit the way it reads smart card information. “When in a sensitive state, more than two principals are not allowed to participate; password input must be protected in the same way that other sensitive data is protected.â€
The information stored on the smart card is generally divided into several parts. Such as: read-only information; only information that can be added; information that can only be updated; information that cannot be read. In this way, some password information can be stored in an unreadable storage area.
If, only the person who knows the password can use the smart card, but if you need to transfer the information on the card to the other place via radio or telephone line, you must have extra protection.
(3) Key management
Key management is actually a way to control the reading of smart card information from the structure of the card and the supported encryption algorithms. "For asymmetric key management, the specifications of ISO 11568 Part IV and Part 5 must be supported; the management of symmetric keys must conform to the specifications of ISO 11568 Part II and Part III. The key algorithm must use an algorithm that has been approved by the specification. And keep the key strictly."
2. Key algorithm of smart card
By encryption, a smart card can translate information into various symbols and the like, and can randomly select one when it is necessary to communicate. This prevention mechanism ensures that both the card and the computer used are authentic and effective, making it almost impossible to steal the transmitted information halfway. The microprocessor smart card has the function of adding/decrypting (rewriting the unreadable things) so that the information stored on the card can be transmitted without fear of leaking.
The encryption technology of smart cards is divided according to whether the key algorithm is disclosed or not. Currently, it can be divided into SKE (Secret Key Encryption: secret key encryption system, also known as symmetric key algorithm) and PKE (Public Key Encryption: public). Key encryption systems, also known as asymmetric encryption algorithms, are two. The difference between the SKE algorithm and the PKE algorithm is mainly: whether the encryption/decrease key is consistent or not.
(1) SKE algorithm
The so-called SKE algorithm means that the encryption key and the decryption key are the same. For security, the keys have to change periodically. Symmetric algorithms are fast, so they are widely used when processing large amounts of data. The key is to ensure the security of the keys.
(2) PKE algorithm
The so-called PKE algorithm means that there is a public key and a private key respectively, the public key is publicized, and the private key is kept secret. The public key and the private key have a one-to-one correspondence. The data encrypted by the public key can be unlocked only by the private key, and the efficiency is lower than that of the symmetric key algorithm.
3. Digital TV reception smart card security
The security of digital TV receiving smart card not only has the basic requirements of the above smart card, but also has other unique security requirements. This is the authentication between the digital TV smart card and the digital TV set-top box.
Four digital TV smart card and set-top box authentication / agreement
Since the micro-processing smart card has a microprocessor that supports the SKE algorithm and the PKE algorithm, and the size of the micro-processing smart card is extremely portable, it must become a CADTV (Cable Digital Tele Vision) network data transmission and identity. A well-certified security module.
1. Digital TV smart card and set-top box certification
Digital TV receives authentication between the smart card and the set-top box, mainly to prevent the use of unauthorized smart cards in the set-top box. The authentication methods mainly include shared key-based identity authentication and certificate-based identity authentication.
At present, the authentication relationship between the digital TV smart card and the set-top box is basically completed by the algorithm specified by the CAS (Conditional Access System) provider of the CADTV broadcasting system. The general authentication relationship has two levels: The first is to establish a simple link relationship between the digital TV smart card and the set-top box, just as the husband and wife match to verify its legal validity; the second is to encrypt the communication between the smart card and the set-top box under the entire digital TV CAS key system, very strict Verify the relationship between the card and the set-top box's rigorous mathematical algorithms to enhance business security.
The strict mathematical algorithm relationship of this verification is derived from the error-free link-level communication protocol provided by the international standard ISO 7816, which is mainly the T=0 protocol and the T=1 protocol. Once the link protocol is established, it can be defined. An application protocol that uses a link to communicate between an application on a card and other applications on the set-top box. ISO and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) jointly regulate such application protocols for two purposes: one is to provide a consistent file system for storing and retrieving information on the card; the other is API (Application Program) Interface: The interface of the application interface that accesses the security services on the smart card.
2. Link level communication
The T=0 protocol attempts to mix the elements of the application protocol with the elements of the link protocol, while the T=1 protocol is equivalent to the data link protocol.
The T=0 protocol of link-level communication is a byte-oriented protocol that acts in a command response manner. In this mode, the connected reader side sends a command to the card, and the card performs the operation commanded by the card reader. And send back a response. In the T=0 protocol, error detection is performed by parity bits. The TPDU (Transport Protocols Data Units) of the T=0 protocol has two different data structures: one is a command sent from the card reader to the card; the other is a response sent by the card to the card reader.
The T=1 protocol is a block-oriented protocol. Error detection in the T=1 protocol is done by LRC (Vertical Redundancy Check), and the algorithm used is defined in ISO 3309. The T=1 protocol uses three different types of blocks, but each block has the same structure.
Five conclusions
With the development of digital TV technology and network technology, commercial activities such as electronic shopping through the Internet will increase. In the future of digital TV applications, smart cards can also be programmed to function as an e-wallet. Used for online shopping and other instant payment services. These commercial activities are often carried out through public networks for data transmission, which puts higher demands on the confidentiality of data during network transmission. These requirements mainly include:
* Encrypt sensitive files so that they cannot get their content even if they intercept the file;
* Ensure the integrity of the data and prevent the interceptor from adding other information to the file;
* Verify the source of data and information to ensure the identity of the sender.
Nowadays, the combination of PKE and SKE is widely used in the industry to meet the above requirements.
references:
1. "Guiding Opinions on Cable Digital TV Middleware" Technical Requirements for the People's Republic of China Radio, Film and Television Industry June 2003
2. "Guidelines for the Application of Cable Digital TV Conditional Access System" Technical Requirements for the People's Republic of China Radio, Film and Television Industry June 2003
3. "Guidelines for the Application of Cable Digital TV Broadcasting Business Information" Technical Requirements for the People's Republic of China Radio, Film and Television Industry June 2003
This is our hot selling FPV RC Car with FPV great experience with four-wheel drive, the tire is made of PVC rubber material, the texture design of the bump makes the Remote control car easy to handle in various road conditions.With 12mm plastic hydraulic shock absorbers and speed can meet 35km/h,let you enjoy the fun of running.Body with PVC material, more drop-resistant, increase vehicle life expectancy.Dual motor driving, more powerful.1000TVL CCD 110 °Mini FPV Camera Seven Colors Adjustable Lamp, real-time back return HD screen details,enhance your operating experience and make your operation more smooth and flexible.
High Speed FPV RC Car,Fast RC Cars,High Speed RC Flying Car,Radio Control FPV RC Car
Airjugar Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.airjugarFPV.com