Problem proposition and solution
In recent years, as wireless terminal tools such as laptops, netbooks, iPADs, iPhones, and smartphones with wireless network cards have become increasingly popular among teachers and students, the space limitations of wired networks have become increasingly prominent.
The increased demand of students for wireless networks not only puts more pressure on the construction of campus network wireless networks, but also puts forward higher requirements for operators who provide mobile wireless networks outside the school.
On the campus, with the popularization of 3G mobile phones and other products among students, the mobile phone base station outside the operator that provides export bandwidth has obviously failed to support the 3G application of student users with increasing data volume. Operators urgently need to build on campus Wireless local area network, and then transmit data through high-speed optical cable to alleviate the data congestion of the base station.
The wireless AP and the corresponding antenna are put into construction by the operator. Using the existing wired backbone network on the campus, by setting up logical channels isolated from each other, it not only ensures the smooth flow of 3G data for the operator, but also provides school teachers and students with wireless throughout the campus With network signals, teachers and students can access the Internet through the operator's account or access information resources on the Internet through the school's account.
This dual-access, dual-authentication, dual-operation wireless network model, through the cooperation between the operator and the campus network, has greatly shortened the construction period of the wireless network project, and also greatly reduced the operating costs of both parties. It alleviates the lack of wireless investment of the school and satisfies the application requirements of the wireless network in the school. Below we will introduce in detail the design principles and implementation methods of this model.
Design Principles
Demand-driven principle
There are two types of users in the dual-access wireless network, one is the operator's user, and the other is the user using the campus network. The number of wireless information points and the amount of information transmitted by users in different areas of the campus are different. Laptops and netbooks are mainly used in study rooms and libraries, while iPAD, iPhone, and smartphones are mainly used in the open areas of the campus. Wait.
Therefore, before the wireless network design, detailed demand research should be conducted to form a demand report, and then the demand report should be fully reviewed and demonstrated. According to the demand report, the logical topology of the school's wireless network is designed. At the same time, the demand report is also a device selection, Basis for selection of agreements, estimation of input costs, schedule planning, etc.
Principle of shared responsibility and shared benefits
Teachers and students use the wireless network to send and receive data, not only through the operator's wireless AP, wireless AC (access controller), wireless router and other equipment, but also through the school's aggregation switch, wired backbone network, core switch, core router and other equipment.
Only if both parties can guarantee the normal operation of their respective equipment, the entire wireless link can be stable and reliable. In terms of Internet tariff, it is necessary to protect the vested interests of the operator and not to harm the interests of schools, teachers and students.
Economic applicability principle
The distance between the location of the wireless AP installation and the AP should not only meet the normal practical needs of teachers and students, but also prevent repeated construction and waste of resources. In terms of equipment selection, domestic equipment with high cost performance should be considered as much as possible. Considering the cost of operation and maintenance, reduce the initial input cost as much as possible.
Safety and reliability principle
All wireless AP devices in the school are connected to the nearest switch by wire. If any AP fails, it will not affect the normal operation of other APs. The wireless redundant structure and backup wireless devices can also enhance the reliability of the wireless network. Wireless AC (Access controller) equipment and MAC-based authentication and encryption technologies can ensure the security of campus wireless networks.
Maintain management transparency
For the operator ’s equipment, the operator ’s administrator has all rights to manage the equipment, while the school ’s administrator only has the right to view the device ’s operating status; for the school ’s equipment, only the school ’s administrator can set it, while the operator ’s administrator Can only be viewed. On the basis of following the management agreement reached by both parties, the normal management and maintenance of the equipment by either party will not affect the operation of the other party's equipment.
Design and implementation
Comparison of Fat AP Architecture Technology and Thin AP Architecture Technology
The AP device in the fat AP architecture technology has advanced wireless network management functions such as user data encryption authentication, Qos, network management, and roaming technology. Fat AP architecture technology has the advantages of flexible network structure, low construction cost, and high network stability. The disadvantages are that the device structure is complex and difficult to centralize management, network security is poor, unified management is not possible, configuration and management costs are high, and user experience is poor.
The AP function in the thin AP architecture technology is simple and cannot work independently, and must be combined with AC (access controller) to use. The entire technical architecture is composed of three parts, namely, thin AP, AC, and wireless network management platform. The thin AP is located at the network access layer and is uniformly configured by the AC. Its role is to connect wireless users to the wireless network.
The thin AP architecture technology has the advantages of global unified management, global unified security, global unified authentication, roaming throughout the network, etc. The wireless network management functions of this technical architecture are centralized on the AC, there is a single point of failure risk, but it can Eliminate risk by using AC backup technology. When there are many wireless APs, thin AP architecture technology is a better choice for designing wireless LAN.
Wireless dual access design and AP deployment
The wireless terminal access process is to first discover active wireless services through active scanning or passive scanning technology, and then establish a wireless connection with the AP that transmits wireless signals. The connection establishment process is that the wireless AP and wireless terminal successfully exchange authentication requests, A series of information frames such as authentication response, association request, and association response. The maintenance of the connection is also by periodically sending or receiving monitoring frames. Stable wireless connection is the prerequisite for data transmission on the wireless network.
For the network architecture of "thin AP + wireless controller", the access design is to design the USSID, radio frequency and authentication method of the AP through the AC. Due to the limited number of APs that the AC can control, in order to avoid users from an AC-controlled AP When entering an AP controlled by another AC, a network interruption occurs due to network reconnection and re-authentication, and roaming needs to be designed between the ACs.
Set two unified SSID names for each AP controlled by the AC, namely ChinaNet and GDSSPT. As shown in Figure 1, ChinaNet provides wireless services for operators, and GDSSPT provides network services to school users. SSIDs with the same name belong to the same VLAN .
The maximum power of the AP radio frequency, the maximum number of users supported, the type of antenna, and the on-site visibility are the main basis for the AP deployment solution. The AP deployment is based on the coverage of the AP signal and the user's network requirements to determine the installation of AP equipment Location and distance between APs.
Wireless dual authentication design and implementation
According to the network architecture, wireless network authentication can be divided into two categories, one is wireless link authentication, and the other is user access authentication. Wireless link authentication is the authentication performed when the wireless terminal establishes a connection with the wireless AP. The result of the authentication is that the connection is successfully established or cannot be established. Link authentication can be divided into open authentication and shared key authentication according to whether the key is used. Open authentication means that the AP agrees to establish a connection as soon as it receives a request, while shared key authentication means that the terminal and the AP must use the same key to establish a connection.
User access authentication is based on the successful establishment of the connection. The network control device authenticates whether the user has the right to access the network. Generally, it can be divided into three authentication methods: pre-shared key authentication (PSK), 802.1X authentication, and MAC address authentication. It is also possible to perform WEB authentication when exporting information from a wireless network in an authentication system in a wired network.
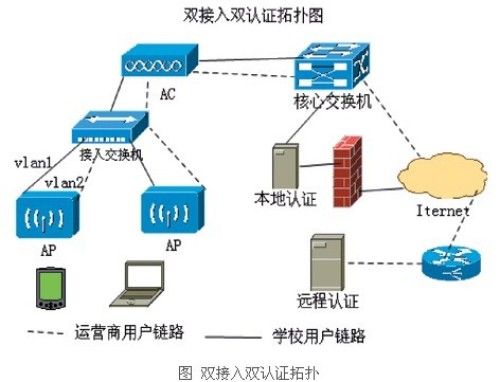
Use the routing functions of the convergence layer and core layer devices in the wired network to route different types of user data information to different authentication systems for user authentication, so as to realize the dual authentication function of the network, as shown in the figure. The data of VLAN1 is routed to the local server for export web authentication. The web authentication server is located at the exit of the campus network. School users can only use the correct account and password to access external resources, and the resources in the school can be used without authentication.
The data information of VLAN2 is routed to the operator's remote RADIUS authentication system for authentication, requiring wireless clients to get the SSID network to use the remote MAC address authentication method to access the Internet. The RADIUS server is responsible for authentication, authorization, and accounting services.
Dual operation security strategy
Currently, wireless devices generally support three encryption technology strategies: WEP encryption, TKIP encryption, and CCMP encryption. The purpose of WEP encryption is to encrypt the data transmitted on the wireless network, hoping to achieve the same security effect as the wired network. According to the method of key generation, it can be divided into static WEP encryption and dynamic WEP encryption.
Static WEP encryption technology uses RC4 streaming technology to encrypt data, while dynamic WEP encryption must be used in conjunction with 802.1X authentication, and the RIDIUS server periodically forces clients to re-authenticate and generate new keys.
TKIP encryption is under the 802.1X / EAP framework. After the authentication server accepts the user's identity, it uses 802.1X to generate a unique master key to process the session and distribute it to the AP and client through a secure channel to form a key architecture management The system can dynamically generate a unique data encryption key through the master key to encrypt the data on the wireless network.
CCMP encryption is based on the AES encryption algorithm, which combines CTR for encryption and an encrypted block link message authentication code for authentication and integrity to provide encryption, authentication, and integrity protection for data transmitted on the wireless network. The AES block encryption algorithm in CMP uses a 128-bit key and a 128-bit block size.
CCMP includes a set of dynamic key negotiation and management methods. Each wireless user will dynamically negotiate a set of keys, and the keys can be updated regularly, further providing the security of the CCMP encryption mechanism. In the encryption process, CCMP will also use a 48-bit PN (Packet Number) mechanism to ensure that each encrypted message will use a different PN, to a certain extent, improve the security of the wireless network.
The LED Jewelry Box with a LED light which can make your jewelry more shine, when you use LED jewelry box to show your ring to your girlfriend, I think she will love it in the moment, and love you. And when you use the LED jewelry box to show your products to your custom, your custom will buy the product right way. So the LED jewelry box may your best choice to attract the attention, you will the brightest in the night.
Brand Name: Jinao
Place of Origin: Guangdong, China(mainland)
Surface Material: Customized
Inner Material: Velvet / foamed plastic
Color: Customized
Size: Multi-size + Customized
Feature: shining
Logo Printing: Customized
Usage: Jewelry Box / Gift Box
Jewelry Box With Led,Special Led Jewelry Box,Jewelry Boxes With Led,Luxury Led Jewelry Box
DongGuan Jinao Packaging Products Co., Ltd , https://www.jinaojewelrybox.com